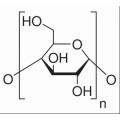
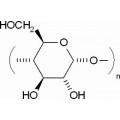
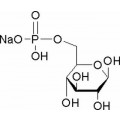
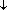抗体和蛋白
A primary antibody directly binds to specific antigens, with high specificity and affinity, for the purposes of purifying or detecting and measuring the antigens. Primary antibodies can either be developed as monoclonal antibodies, which bind to one specific epitope on the antigen, or polyclonal antibodies, which bind to multiple different epitopes on the antigen, using animals as the hosts, typically: rats, rabbits, mice, goats, and other species.
Primary antibodies can be raised against any antigen of research interest, including: proteins, peptides, carbohydrates, and other small molecules. Primary antibodies can also be raised to recognise post translational modifications such as phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, and glycosylation. As such, primary antibodies are great tools to analyse components of living cells at the molecular level and identify proteins that may be involved in or may cause disease.
|
Order details
|
Cat. No. MC11003
|
| ...
|
|
Order details
|
Cat. No. MC11008
|
| ...
|
|
Order details
|
Cat. No. MC11004
|
| ...
|
|
Order details
|
Cat. No. MC11006
|
| ...
|
|
Order details
|
Cat. No. MC11007
|
| ...
|
|
Order details
|
Cat. No. mc11013
|
| ...
|
|
Order details
|
Cat. No. MC11017
|
| ...
|
|
Order details
|
Cat. No. MC11010
|
| ...
|
|
Order details
|
Cat. No. MC11012
|
| ...
|
|
Order details
|
Cat. No. MC11025
|
| ...
|